TL;DR
- Walks through two Python options for XML: ElementTree first, then Minidom.
- ElementTree: quick to load/parse XML and extract tag/text, good default for most tasks.
- Minidom: full DOM-style navigation and node control when you need detailed structure handling.
- Side-by-side code examples help you choose the right parser for your workflow.
Parsing XML in Python is essential for developers dealing with structured data, web services, or configuration files. XML, or Extensible Markup Language, remains a widely used format for storing and exchanging data across different systems. Python offers powerful and user-friendly libraries that make navigating, extracting, and modifying XML data straightforward and efficient.
In this article, we’ll explore practical methods to parse XML using Python, highlighting easy-to-follow examples and helpful tips to streamline your data processing tasks.
Python XML Parsing Modules
There are two main modules for parsing XML with Python.
xml.etree.ElementTreehelps us format XML data in a tree structure, which is the most natural representation of hierarchical data. TheElementdata type allows data storage of a hierarchical data structure in memory.xml.dom.minidomis used by people who are proficient with DOM (Document Object Module). It often starts with converting XML into a DOM.
Let’s discuss each of them in detail.
ElementTree
ElementTree is a class that wraps the element structure and allows the conversion to and from XML. It has the following properties:
- Each element that is present in the element module will consist of a tag that represents the type of data being stored.
- The attributes that are stored are Python dictionaries.
- A text string consisting of the information that needs to be displayed.
- An optional tail string.
- Child elements that consist of other specific data.
Now, we will learn how this module can be used for parsing an XML document.
Parsing with ElementTree module
There are two ways to parse the XML file with this module:
- Using the Parse function
- Using fromstring() function
Parsing with the Parse function
Consider this sample XML data. I am naming this file as sample.xml.
<note>
<to>User</to>
<from>Admin</from>
<message>Hello from XML!</message>
</note>
Now, let’s write some Python code to parse the data from this XML file using the Parse function. I am naming this file as pyxml.py.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Parse the XML file
tree = ET.parse('sample.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
# Access elements
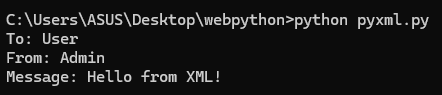
print("To:", root.find('to').text)
print("From:", root.find('from').text)
print("Message:", root.find('message').text)
Let me explain to you this code step by step
- First, we imported Python’s built-in XML parsing library
ElementTree. - We are loading the file
sample.xmland heretreebecomes anElementTreeobject representing the full XML structure. - The third line retrieves the top-level (root) element of the XML, which is
<note>in this case. - Finally, we search for the
<to>tag inside the root and get its text content. The same applies for<from>and<message>.
Once you run this code, you will get parsed data.
Parsing with fromstring() function
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
xml_data = '''
<note>
<to>User</to>
<from>Admin</from>
<message>Hello from XML!</message>
</note>
'''
# Parse the XML string
root = ET.fromstring(xml_data)
# Access elements
print("To:", root.find('to').text)
print("From:", root.find('from').text)
print("Message:", root.find('message').text)
- 1. Import the
ElementTreemodule asET. - 2. Define an XML string stored in the
xml_datavariable. - 3. Use
ET.fromstring(xml_data)to parse the XML string into an element tree. - 4.
rootnow represents the<note>element (root of the XML structure). - 5. Use
root.find('tag').textto extract text from<to>,<from>, and<message>tags. - 6. Print the extracted values.
Minidom
minidom (short for Minimal DOM implementation) It is a lightweight XML parser in Python that provides a Document Object Model (DOM) interface to XML documents. It’s part of Python’s standard library under xml.dom.
- Allows navigation and modification of XML elements, attributes, and text nodes.
- Suitable for small to moderately sized XML documents.
- Access elements by tag name using
getElementsByTagName().
Parsing with the Minidom module
Just like the Elementtree module, this module also has two methods for parsing.
- Using the
Parse()function. - Using
parseString()function.
Parsing with the Parse function
Consider this sample.xml file.
<note>
<to>User</to>
<from>Admin</from>
<message>Hello from XML!</message>
</note>
Now, let’s write some Python code to parse this data.
from xml.dom import minidom
# Parse the XML file
doc = minidom.parse('example.xml')
# Access elements
to = doc.getElementsByTagName('to')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
from_ = doc.getElementsByTagName('from')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
message = doc.getElementsByTagName('message')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
# Print values
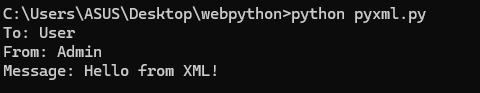
print("To:", to)
print("From:", from_)
print("Message:", message)
1. Import the minidom module from xml.dom.
2. Use minidom.parse('example.xml') to read and parse the XML file.
3. doc now holds the parsed XML document object.
4. Use getElementsByTagName('tag')[0] to access the desired element.
5. Access the text inside the tag using .firstChild.nodeValue.
6. Print the extracted values for <to>, <from>, and <message>.
Once you run this code, you will get this.
Parsing with the parseString() function
from xml.dom import minidom
xml_data = '''
<note>
<to>User</to>
<from>Admin</from>
<message>Hello from XML!</message>
</note>
'''
# Parse the XML string
doc = minidom.parseString(xml_data)
# Access elements
to = doc.getElementsByTagName('to')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
from_ = doc.getElementsByTagName('from')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
message = doc.getElementsByTagName('message')[0].firstChild.nodeValue
# Print values
print("To:", to)
print("From:", from_)
print("Message:", message)
1. Import minidom from the xml.dom module.
2. Define an XML string and store it in xml_data.
3. Use minidom.parseString(xml_data) to parse the XML string into a document object.
4. Access the first <to>, <from>, and <message> elements using getElementsByTagName('tag')[0].
5. Extract the text inside each tag using .firstChild.nodeValue.
6. Print the extracted values.
You will get the same response once you run this code.
Key Takeaways:
- Shows how to parse and navigate XML data using Python.
- Demonstrates different Python libraries for XML parsing (e.g., ElementTree, lxml).
- Provides example code to extract specific elements and attributes from XML.
- Explains how to handle XML with namespaces and hierarchical structures.
- Useful for working with APIs, RSS feeds, and structured data formats.
Conclusion
Parsing XML in Python is straightforward thanks to built-in libraries like ElementTree and minidom. Whether you’re working with XML files or raw XML strings, both modules offer simple methods parse() and fromstring() or parseString(), to access and manipulate XML data efficiently. While ElementTree is more Pythonic and suited for most use cases, minidom provides a complete DOM-style interface for those needing more control. By understanding both, you can choose the right approach depending on your project’s needs.