TL;DR
- Shows how to scrape Baidu search results using Python.
- Uses Scrapingdog’s Baidu Search API to fetch structured
JSONwithout dealing with proxies, CAPTCHAs, or parser maintenance. - Results include: title, link, snippet, and ranking from the Baidu SERP.
- Python examples demonstrate how to call the API and parse the response easily.
When it comes to search engine data, most tutorials focus on Google, but what if your target audience is in China? That’s where Baidu, the country’s leading search engine, comes in. Whether you’re tracking keyword rankings, monitoring competitors, or gathering localized insights, scraping Baidu search results can give you access to valuable, real-time data that isn’t available elsewhere.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to scrape Baidu search results using Python, step by step no prior scraping experience required.
Why scrape Baidu Search Results?
Baidu dominates the Chinese search market, holding over 75% share, making it the go-to source for online information in China. Scraping Baidu search results allows developers, marketers, and researchers to gain deep insights into the Chinese web ecosystem. You can:
- 🔍 Track keyword rankings for SEO in Chinese markets.
- 🏢 Monitor competitors and analyze their visibility in Baidu’s SERPs.
- 📰 Collect news and content trends relevant to specific industries.
- 📊 Build datasets for training AI and NLP models with localized content.
- 🌏 Understand market behavior and consumer interests unique to China.
In short, if your business or research involves Chinese audiences, scraping Baidu is one of the most direct and effective ways to access that data.
Why use Scrapingdog to Scrape Baidu search results?
Scraping Baidu directly can be challenging due to its strict anti-bot systems, IP rate limits, and frequent layout changes. That’s where Scrapingdog comes in, and it takes care of all the heavy lifting like proxy rotation, CAPTCHA handling, and response parsing. Instead of worrying about blocked requests or HTML changes, you can simply send a query and receive structured, ready-to-use data.
With Scrapingdog’s Baidu Search API, you get clean JSON output containing titles, links, and snippets, and all accessible in one simple API call. It’s fast, reliable, and built to scale, whether you’re scraping a few keywords for SEO or running large-scale data collection for AI and analytics. In short, it saves developers hours of setup time while maintaining accuracy and consistency across requests.
Prerequisite
I hope you have already installed Python 3.x on your machine; if not, you can download it from here.
Now, create a folder by any name you like. I am naming the folder as webpython. Inside this folder, create a Python file and name it whatever you like. Now, install requests library inside this folder. We will use this to make an HTTP connection with the host website.
The final step is to sign up for Scrapingdog’s trial pack. You’ll receive 1,000 free credits upon signup, which you can use to test any of Scrapingdog’s APIs.
Scrape Baidu Search page with Python
After signup on Scrapingdog you will be redirected to your dashboard. You will find a Baidu Search API over there.
Once you click on it, you will see a scraper where you just need to pass a sample query, and it will pull the data and return it to you in neat JSON format.
For this tutorial, we will pass the query as web scraping. After passing the query you will get a ready Python code; you just have to copy that and paste it in your Python file.
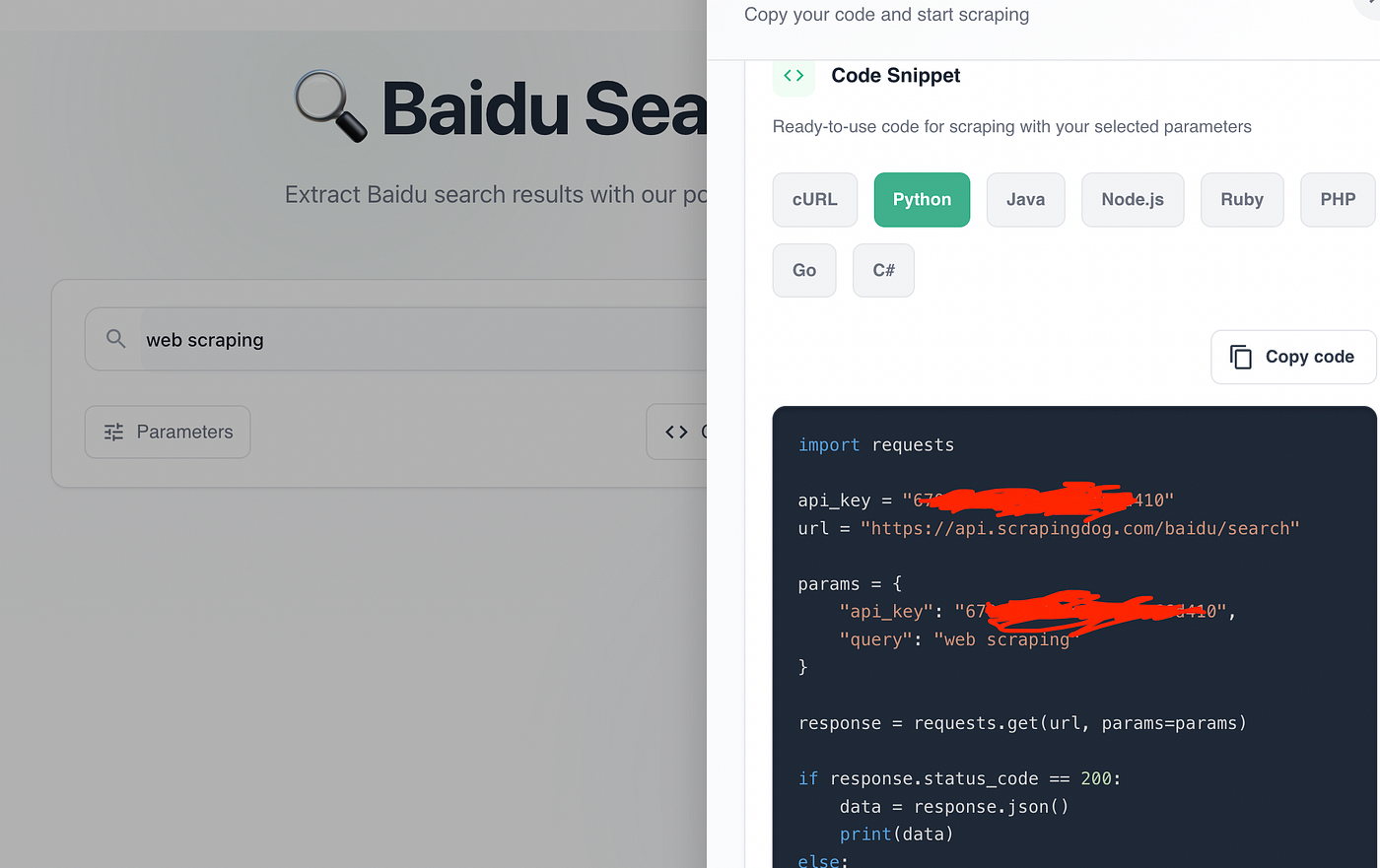
import requests
api_key = "your-api-key"
url = "https://api.scrapingdog.com/baidu/search"
params = {
"api_key": api_key,
"query": "web scraping"
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
print(data)
else:
print(f"Request failed with status code: {response.status_code}")
Let me explain this code step-by-step.
- First we have imported the
requestslibrary. This will be used for making the HTTP connection with the host website. - Then we are storing the API key and the Scrapingdog’s Baidu Search API URL.
- Then we are making the GET request with the help of
requestslibrary. - If the request is successful (status 200), it prints the search results.
- If it fails, it prints the error status code.
Once you run the code you will get this parsed JSON data.
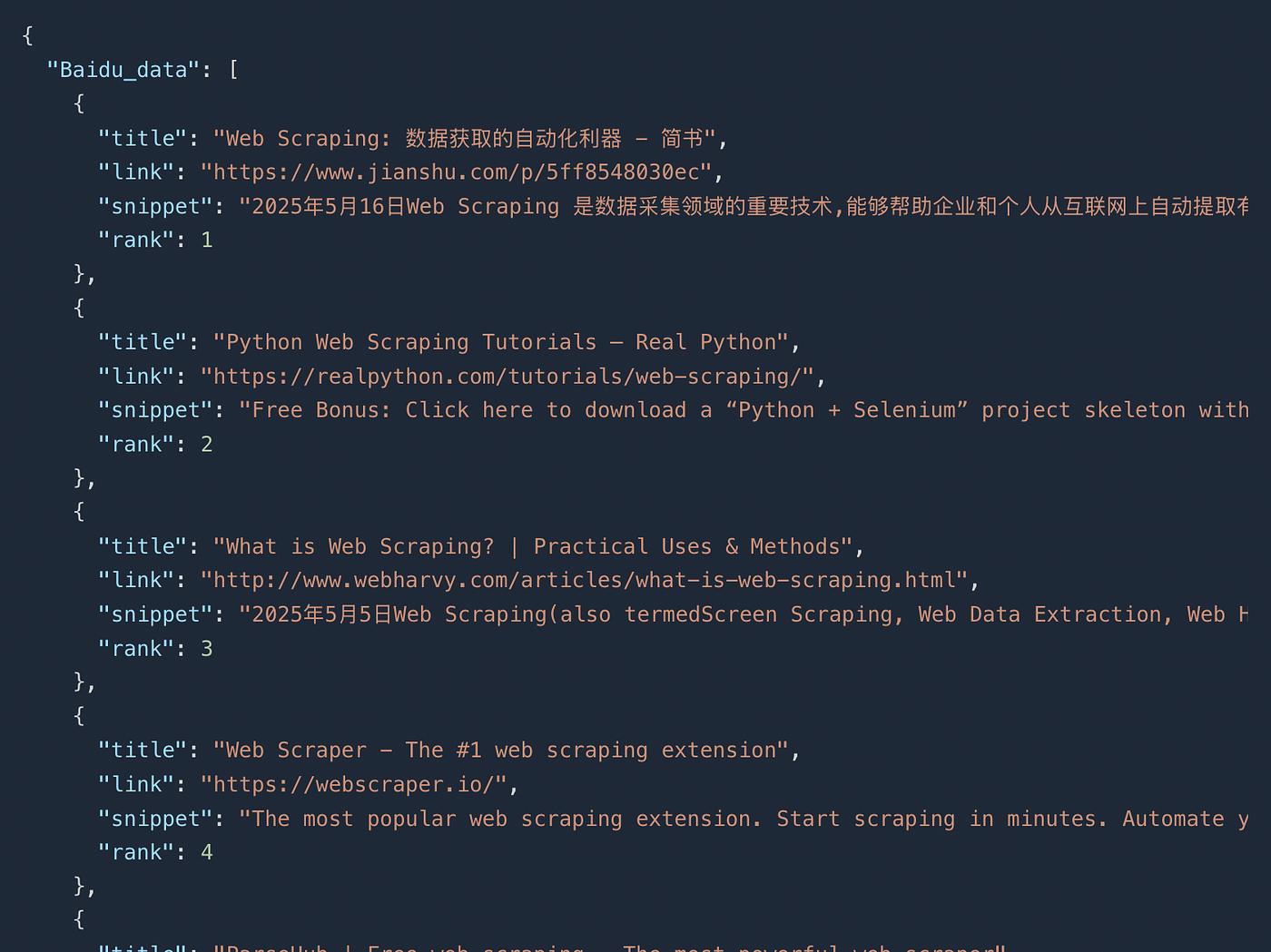
In this JSON response you will find the title, link, snippet and rank of the result.
Key Takeaways:
- You can programmatically extract Baidu search results using Scrapingdog’s Baidu Search API.
- The API returns clean, structured SERP data without manual HTML parsing.
- Using an API solves common challenges like proxy rotation and anti-bot measures.
- You can customize search parameters like language, pagination, and filters.
- This approach scales well for data collection and analytics.
Conclusion
Scraping Baidu data doesn’t have to be complex or time-consuming. With Python and Scrapingdog’s Baidu Search API, you can easily extract clean, structured data from Baidu’s search results without dealing with IP bans, CAPTCHAs, or changing HTML layouts. Whether you’re monitoring keyword trends, gathering localized content, or powering AI applications, this API makes it effortless to access reliable Baidu search data at scale.
In short, instead of spending hours maintaining scrapers, you can focus on what really matters — analyzing and using the data to make smarter decisions. Start your free trial on Scrapingdog today and automate Baidu scraping in just a few lines of Python.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1: Is it legal to scrape Baidu search results?
Yes, scraping publicly available Baidu search results is generally allowed. However, you should always follow Baidu’s terms of service and local data regulations when using the data commercially.
2: Can I scrape Baidu without getting blocked?
Direct scraping often leads to IP bans and CAPTCHAs. Scrapingdog handles proxies and CAPTCHAs automatically, so you can scrape Baidu reliably.
3: What data can I extract from Baidu using Scrapingdog?
You can extract the title, URL, snippet, and ranking position in structured JSON format.
4: Can Scrapingdog handle large-scale Baidu scraping?
Yes, Scrapingdog is built for scale and supports both small and high-volume Baidu scraping use cases.